Written by Harry Roberts on CSS Wizardry.
Desk of Contents
In relation to community efficiency, there are two principal limiting elements that
will sluggish you down: bandwidth and latency.
Bandwidth is outlined as…
…the utmost price of knowledge switch throughout a given path.
Usually talking, elevated bandwidth is simply notably helpful if you’re
transferring or downloading massive information. When you’re streaming video, the
distinction between a 2Mb connection and a 20Mb connection will certainly be
appreciated. When you’re searching the online—with most pages constructed of a lot
smaller information—then the identical change in bandwidth is probably not felt fairly as a lot.
Latency is outlined as…
…how lengthy it takes for a bit of knowledge to journey throughout the community from one
node or endpoint to a different.
The place bandwidth offers with capability, latency is extra about velocity of
switch. As an internet person—usually transferring plenty of smaller
information—reductions in latency will virtually all the time be a welcome enchancment.
So, though it’s extensively accepted that, at the very least for normal net searching,
latency is the larger bottleneck, it nonetheless pays to concentrate on whether or not it’s
latency or certainly bandwidth that’s slowing down a selected file.
On this fast submit, I wish to share a bit of DevTools tip that I am going via in
my efficiency workshops: a easy strategy to rapidly and roughly work out whether or not
your property would profit most from a rise in bandwidth or a discount in
latency, which really brings me onto my first level:
It’s one thing of a misnomer to make use of phrases like enhance in bandwidth
and discount in latency
. We don’t actually have the flexibility to easily
‘enhance bandwidth’—though that might be good!—so what we’re actually trying
to do is cut back the quantity of switch. Equally, there isn’t a lot we are able to do to
actually ‘cut back latency’, however we are able to keep away from
latency
by maybe shifting our property nearer to the shopper (e.g. a CDN) or mitigating
community overhead (e.g. with Useful resource Hints).
Use Massive Request Rows
With a view to make use of this little tip, we’re going to want to allow Massive
Request Rows (1) in Chrome’s Community panel. It will then double up the peak
of every entry in out waterfall chart, thus displaying a bit of extra element (2).
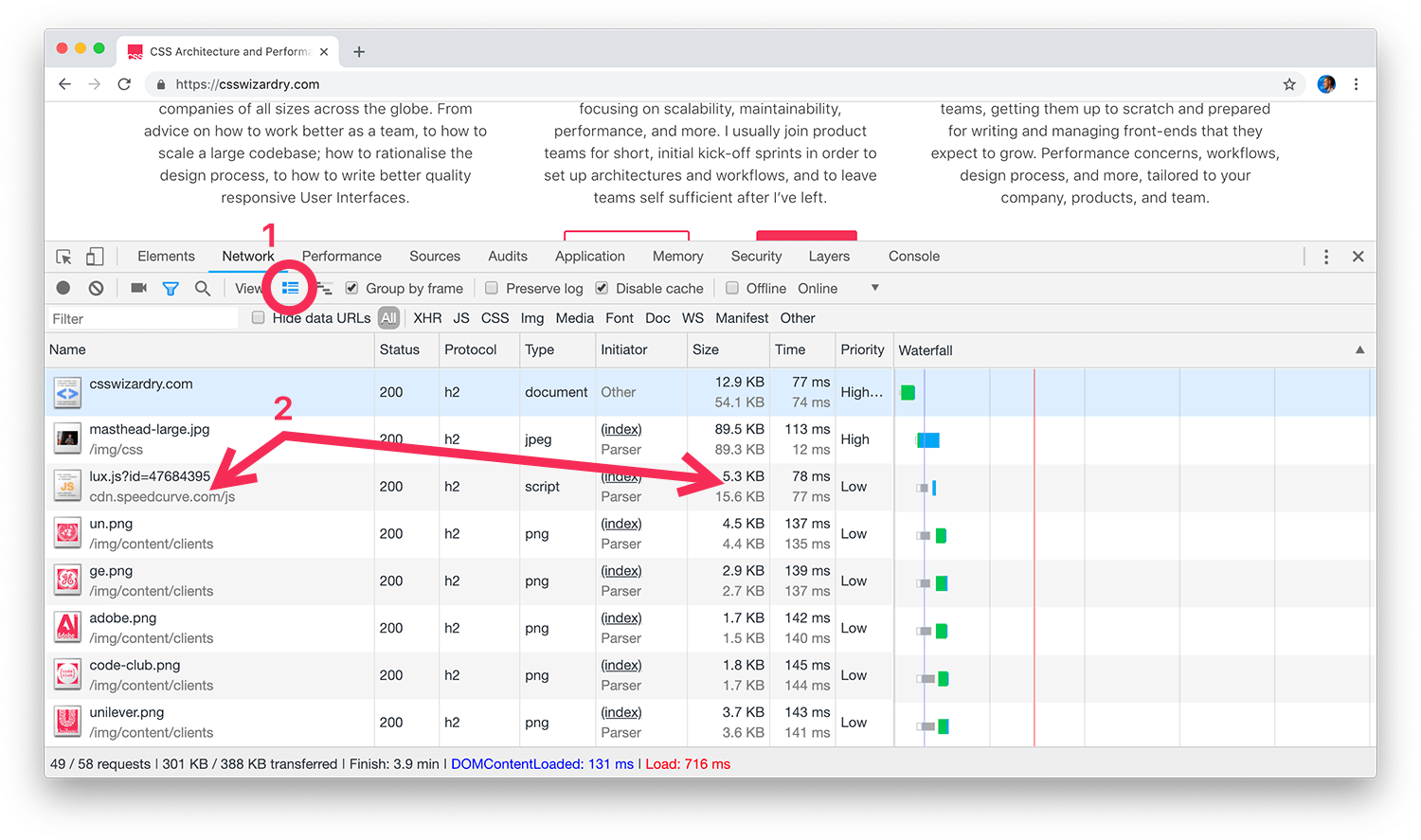
Why this isn’t the default view, I’ll by no means know—there’s a lot helpful further
data right here!
- Within the Title column: In addition to seeing the identify of the useful resource, we now
additionally see both its full file path or its area (if relevant). This permits
me to rapidly and simply confirm whether or not a useful resource is a primary or third
occasion. - Within the Dimension column: We now get introduced with two values. The highest,
darker quantity is the variety of KB that had been transferred over the wire; the
decrease, lighter quantity reveals the variety of KB that had been endured to disk.
A big distinction between these two numbers means that Gzip or Brotli was
current, or a smaller distinction would possibly present the overhead of HTTP headers and
cookies. - Within the Time column: The highest worth is complete time taken from dispatching
the request to having downloaded your entire response. The second worth is the
quantity of that point spent on community negotiation (useful resource scheduling,
connection overhead, TTFB). This decrease quantity is successfully your latency.
That is the column we wish to concentrate on for this text.
The Time Column
There are lots of completely different phases concerned in getting from the purpose of
requesting a file till we’re capable of start downloading it. As soon as sources have
been found, their outgoing requests might should be scheduled, the browser
would possibly must carry out a DNS lookup to find out the useful resource’s origin’s IP
deal with, we’ll then must open up a TCP connection to that origin, hopefully
we’re working over a safe connection that can incur some TLS negotiation, and
then as soon as we’re on the server we cope with Time to First Byte
(TTFB), which
contains time spent on the server and the time taken for the primary byte of knowledge
to traverse the community and find yourself again on the machine.
That’s lots of work, and with smaller information, it could be unsurprising to study
that negotiating all of that community overhead can usually take longer than
the content material obtain itself.

instance’s sake—please don’t learn an excessive amount of into any of the particular numbers right here.
It’s for illustrative functions solely.
Let’s take one other take a look at our screenshot above. Concentrate on the primary entry, the
HTML payload for csswizardry.com. In its Time cell you’ll see a complete
period of 77ms, and a latency worth of 74ms. Subtracting the underside from the
prime worth provides us 3ms. It took solely 3ms to obtain this file, but 74ms to
negotiate the community.
Put one other means, latency price us 24.6× greater than bandwidth for this useful resource.
By far the largest limiting issue right here was latency.
Put one other different means, decreasing the dimensions of this file is unlikely to make it
arrive any sooner. This isn’t a file whose dimension we should always look to optimise.
Take a look at the second entry, masthead-large.jpg. Taking its complete worth of 113ms
and subtracting its latency of (a really miniscule!) 12ms, we’ll see that 101ms
was spent downloading this file.
Put one other means, bandwidth price us 8.4× greater than latency. This can be a useful resource
the place a discount in filesize would result in faster supply.
Wanting on the subsequent entry, lux.js from SpeedCurve,
we’ll see a complete time of 78ms and a latency rely of 77ms. Only one millisecond
to obtain this file—superb! Lowering its dimension is basically going to make so
little distinction.
Lastly, trying on the final 5 picture requests, we see that each one of their
latency occasions sit round 140ms whereas their obtain occasions are at 2ms. If
I needed to hurry up the supply of those photos, I’m unlikely to get any actual
positive factors via optimising them additional.
Vital Concerns
The waterfall I used as a demo was precisely that—a demo. It’s very important that you just run
your personal checks a number of
occasions and throughout
a variety of various community circumstances to evaluate how key sources reply.
rule of thumb to recollect is that, for normal net searching, enhancements
in latency could be extra helpful than enhancements in bandwidth, and that
enhancements in bandwidth are seen extra when coping with bigger information.

